Found 4 results
Open Access
Article
23 April 2025Socio-Economic and Environmental Impacts of Jamrani Irrigation Dam Project, Kumaon Himalaya, India
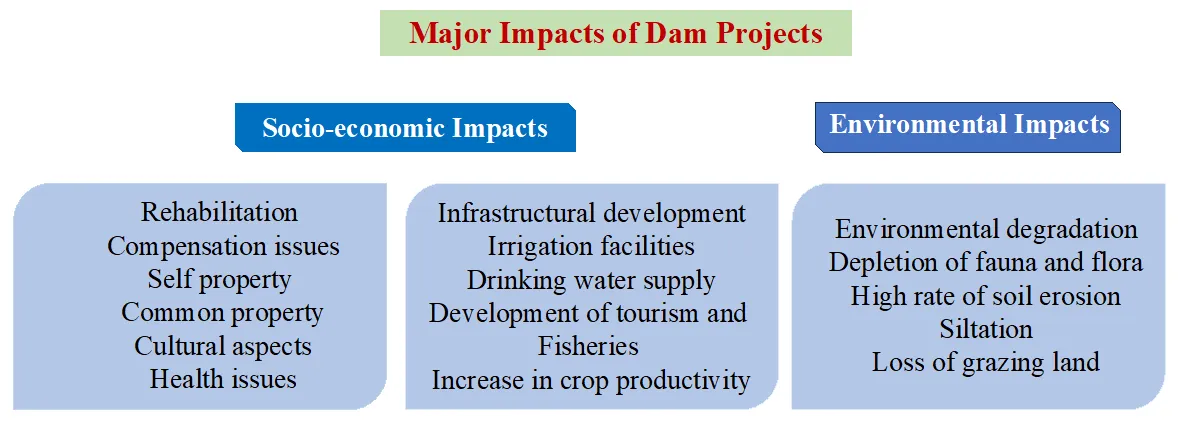
This paper examines the economic and environmental impacts of the proposed Jamrani Irrigation Dam Project on the upstream and downstream areas. This study is primarily empirical, and a case study of six villages was conducted. A total of 415 households are being affected—fully and partially, due to the construction of the dam, out of which 122 heads of households were interviewed. A structured questionnaire was constructed, and the heads of households were asked about the socio-economic and environmental impacts of the proposed dam project. Furthermore, a detailed perception study of these households was conducted. Secondary data related to the size of the dam project, various land uses being affected by the dam, its socio-economic and environmental impact, and the most beneficial sectors were collected from the irrigation department, Government of Uttarakhand’s report 2020. In addition, socio-economic data from 415 households were collected from the same source. This study reveals that the dam project will have many favourable economic impacts in terms of supplying ample water for drinking and irrigation, electricity generation, development of infrastructural facilities and tourism, and the Gaula River flood control. On the other hand, the dam project will lead to land degradation, depletion of faunal and floral resources, soil erosion, and finally, the rehabilitation of the affected people. This study suggests that the proper use of technology and a suitable rehabilitation policy will make the project successful.
Open Access
Article
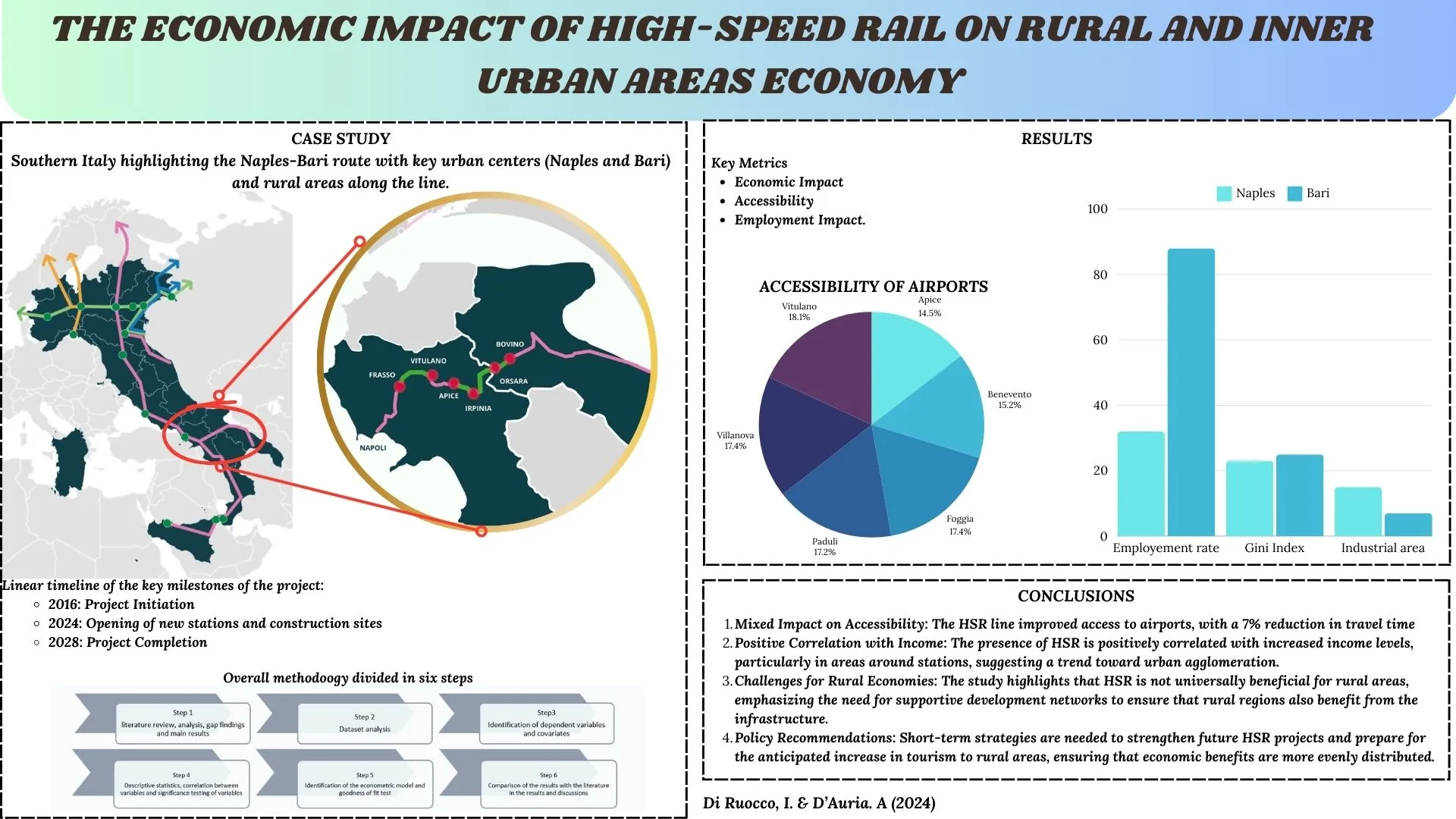
03 September 2024The Economic Impact of High-Speed Rail on Rural and Inner Urban Areas Economy: The Case Study of HSR Naples-Bari in South of Italy
High-speed rail (HSR) has revolutionized global transportation by providing fast, reliable, and efficient city-to-city travel. While its urban benefits are well-documented, the potential advantages for rural development are often overlooked. The high-speed rail project on the Naples-Bari route in Southern Italy aims to connect the urban centers of Naples in Campania and Bari in Apulia, traversing inland and rural areas. Initiated in 2016 and planned for completion in 2028, this project is anticipated to deliver numerous benefits. The purpose of this research is to examine the largely overlooked high-speed rail (HSR) in Southern Italy from an economic and territorial perspective and to determine whether it can sustainably promote rural development in the areas along the railway line. This study examines whether the HSR line will enhance economic activities, strengthen industries, and improve spatial accessibility in rural areas. Using a 2020 dataset covering 25 municipalities along the railway line, including those with stations and construction sites projected to open by 2024, three regression models were employed to estimate potential improvements in income and employment. The findings indicate mixed results: access time to airports improves, decreasing by 7%, while access to ports does not see similar benefits. Income shows a positive correlation with HSR, increasing with population growth around stations, suggesting a trend towards urban agglomeration. However, the study underscores that HSR is not universally beneficial for rural economies and that supportive development networks are crucial. Policies should adopt short-term strategies to strengthen future HSR projects and prepare for the anticipated surge in mass tourism to rural areas.
Open Access
Article
31 May 2024Advancing Green Infrastructure Solutions in Rural Regions: Economic Impacts and Capacity Challenges in Southwest Ontario, Canada
Green infrastructure (GI) is a growing topic in urban planning, asset management, and climate change adaptation. However, rural regions have been under-represented in the discourse. This paper explores the benefits and challenges associated with the implementation and management of GI through a regional study of rural communities in southwestern Ontario. Our focus concerns the inter-relationships between GI, economic resilience, and the development of rural places. Findings show rural communities benefit from GI initiatives like natural stormwater management, park naturalization, and natural heritage restoration, which provide low-cost municipal services, conserve agricultural soils, and contribute to the amenity appeal of rural places. Challenges surrounding awareness, organizational capacity, and environmental regulation have slowed the uptake of GI and led to inconsistencies across jurisdictions. A mix of supportive policies, funding of demonstration projects with economic monitoring, and training to build professional capacity will advance the use and efficacy of GI across rural regions.
Open Access
Perspective
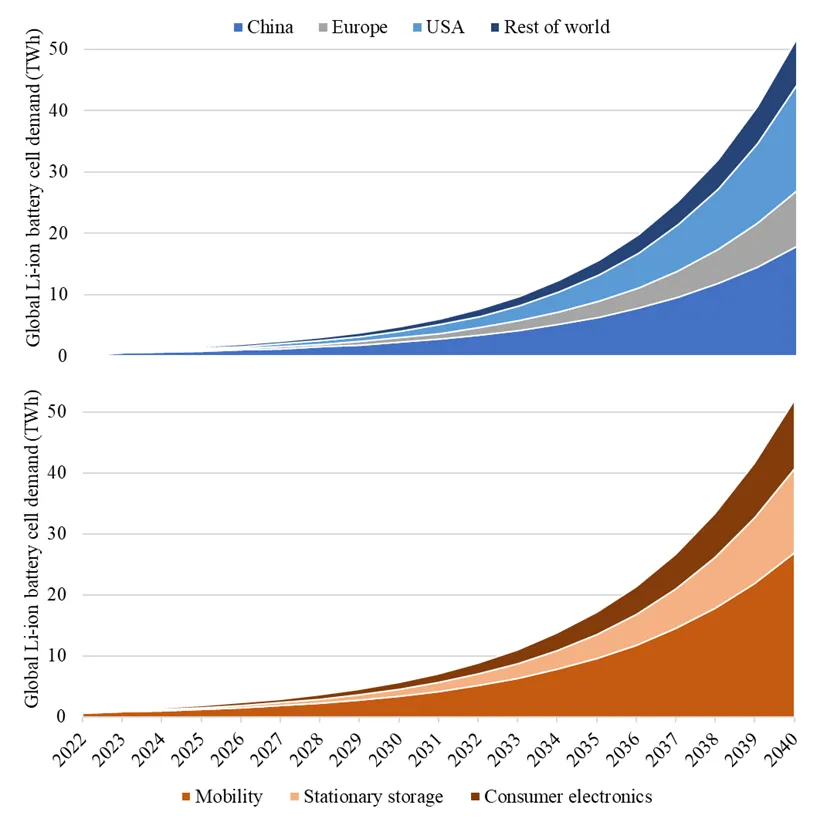
13 September 2023Estimate of Economic Impact of EVs Li-ion Batteries Recovery
Nowadays, increasing attention is directed towards the sustainable use of raw materials. For a circular economy, recovery from spent devices represents a fundamental practice. With the transition to electric mobility, an increasing number of devices powered by lithium batteries are produced. Indeed, this is the fastest growing sector producing spent batteries, which are an important secondary source of critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, graphite, and nickel. Therefore, this work aims to quantify the economic impact of recovering raw materials from lithium batteries used in the electric vehicles sector. Based on the chemical composition of the various lithium batteries and their market diffusion, the intrinsic economic value of this waste has been estimated to be around 6500 €/ton. Starting from the literature data on the global energy demand from lithium batteries and deriving the trend of their specific energy over time, the mass of material introduced into the market annually is estimated to reach 60 Mton/year by 2040. The annual amount of end-of-life lithium batteries was calculated by applying the Weibull distribution to describe the probability of failure, yielding 10 Mton/year by 2040. Finally, based on these results, the economic impact of the recovery market was assessed for two different scenarios.