Found 2 results
Review
21 December 2023TANGO1 Dances to Export of Procollagen from the Endoplasmic Reticulum
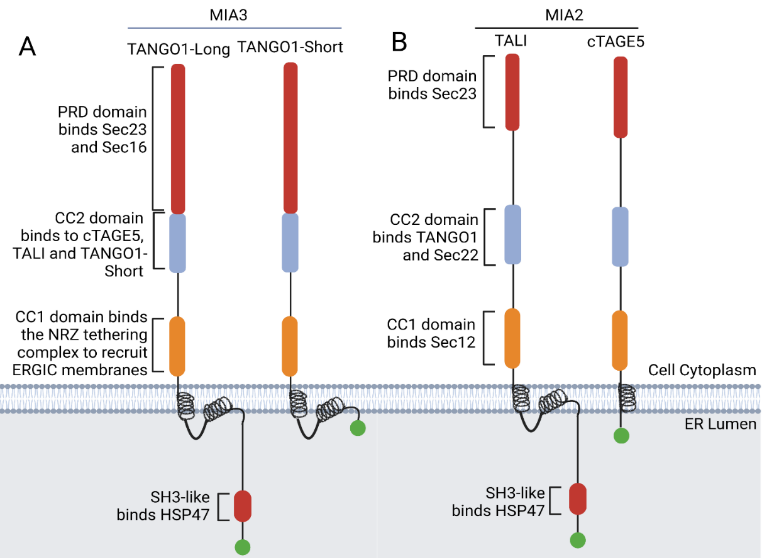
ABSTRACT: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to Golgi secretory pathway is an elegantly complex process whereby protein cargoes are manufactured, folded, and distributed from the ER to the cisternal layers of the Golgi stack before they are delivered to their final destinations. The export of large bulky cargoes such as procollagen and its trafficking to the Golgi is a sophisticated mechanism requiring TANGO1 (Transport ANd Golgi Organization protein 1. It is also called MIA3 (Melanoma Inhibitory Activity protein 3). TANGO1 has two prominent isoforms, TANGO1-Long and TANGO1-Short, and each isoform has specific functions. On the luminal side, TANGO1-Long has an HSP47 recruitment domain and uses this protein to collect collagen. It can also tether its paralog isoforms cTAGE5 and TALI and along with these proteins enlarges the vesicle to accommodate procollagen. Recent studies show that TANGO1-Long combines retrograde membrane flow with anterograde cargo transport. This complex mechanism is highly activated in fibrosis and promotes the excessive deposition of collagen in the tissues. The therapeutic targeting of TANGO1 may prove successful in the control of fibrotic disorders. This review focuses on TANGO1 and its complex interaction with other procollagen export factors that modulate increased vesicle size to accommodate the export of procollagen.
Article
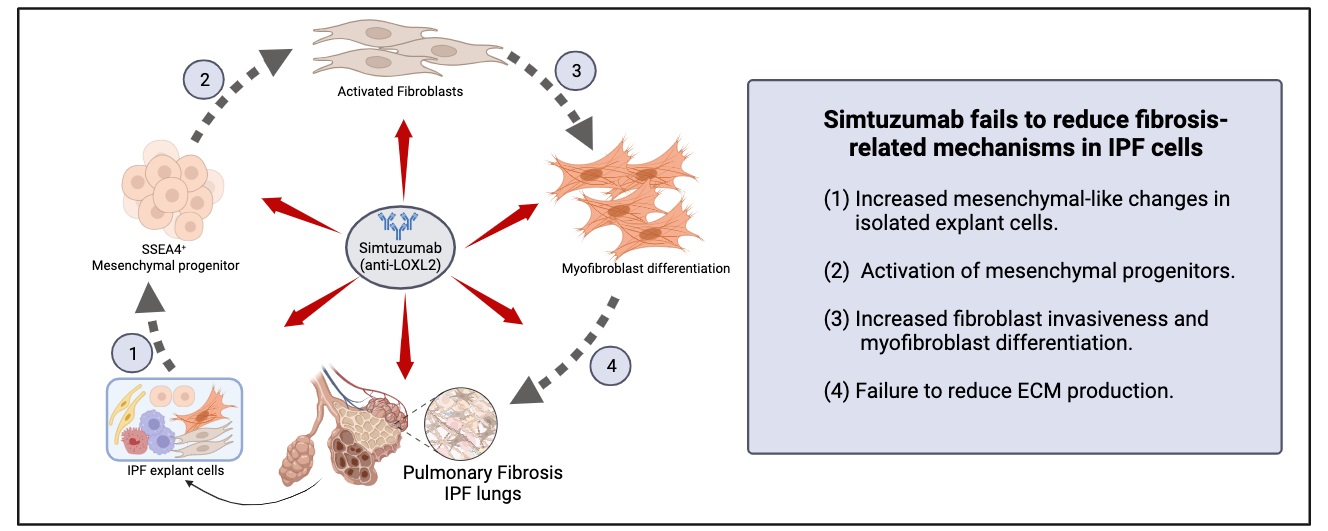
28 November 2023Translational Studies Reveal the Divergent Effects of Simtuzumab Targeting LOXL2 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
The composition of extracellular matrix (ECM) is altered during pathologic scarring in damaged organs including the lung. One major change in the ECM involves the cross-linking of collagen, which promotes fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. We examined the role of lysyl oxidase (LOX)-like 2 in lung progenitors and fibroblasts cultured from normal or IPF lung samples and in a humanized mouse model of IPF using a monoclonal antibody (Simtuzumab). Primary lung fibroblasts from normal donor lungs and IPF lung explants were examined for expression of LOXL2. Targeting LOXL2 with Simtuzumab on normal and IPF fibroblasts was examined both in vitro and in vivo for synthetic, functional, and profibrotic properties. LOXL2 was increased at transcript and protein level in IPF compared with normal lung samples. In a dose-dependent manner, Simtuzumab enhanced differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Inhibition of LOXL2 also enhanced fibroblast invasion and accelerated the outgrowth of fibroblasts from dissociated human lung cell preparations. Finally, preventative or delayed delivery of Simtuzumab enhanced lung fibrosis in a humanized mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. Consistent with its failure in a Phase 2 clinical trial, Simtuzumab exhibited no therapeutic efficacy in translational in vitro and in vivo assays.