Found 2 results
Article
27 September 2024Evaluation of the Efficacy of Chinese Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines against the Delta Variant in the Nanjing Outbreak: A Cohort Study
Background: The strains of COVID-19 are constantly mutating, and the effectiveness of Chinese inactivated vaccines against the COVID-19 Delta variant has not been described clearly. Methods: The clinical data of patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant in the 2021 Nanjing outbreak were retrospectively reviewed. Results: There were 212 patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant (unvaccinated, n = 56, 26.42%; vaccinated, n = 156, 73.58%) included in our cohort study. The median age was 45.5 (38, 53) years old. Eighty-seven subjects (41.04%) were airport staff, and 94 patients (44.34%) in 32 families were infected. There were 53 (25.00%) and 103 (48.58%) cases with one-dose and two-dose vaccination, respectively, and 55 (25.94%), 147 (69.34%) and 10 (4.72%) had mild, moderate and severe symptoms, respectively. The duration of viral shedding, or viral shedding time (VST), was significantly longer in unvaccinated individuals compared to vaccinated individuals (p = 0.0008). Moreover, the duration was significantly longer in patients who received one vaccine dose than those who received two doses (p < 0.0001). The mild patients had significantly shorter VSTs than the moderate subjects (p < 0.0001). Disease severity and vaccination dose were independent predictors for VST by Cox regression models. Conclusions: These results suggest that two-dose vaccination could reduce VST in patients with the COVID-19 Delta variant. Chinese inactivated vaccines may decrease the disease severity of cases with the COVID-19 Delta variant.
Perspective
07 March 2023Pulsed Ultraviolet C as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19
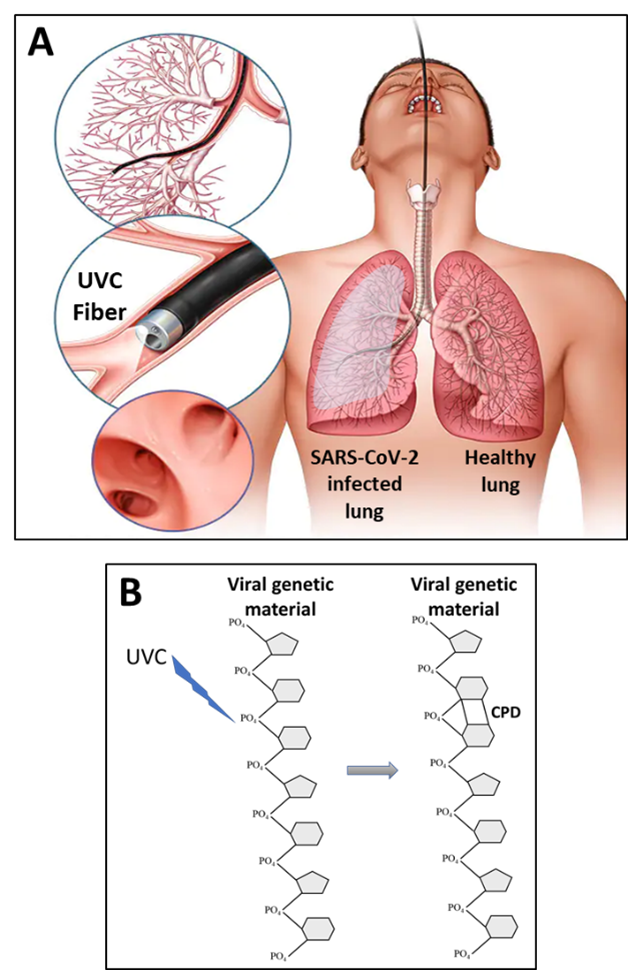
Currently, low dose radiotherapy (LDRT) is being tested for treating life-threatening pneumonia in COVID-19 patients. Despite the debates over the clinical use of LDRT, some clinical trials have been completed, and most are still ongoing. Ultraviolet C (UVC) irradiation has been proven to be highly efficient in inactivating the coronaviruses, yet is considerably safer than LDRT. This makes UVC an excellent candidate for treating COVID-19 infection, especially in case of severe pneumonia as well as the post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis. However, the major challenge in using UVC is its delivery to the lungs, the target organ of COVID-19, due to its low penetrability through biological tissues. We propose to overcome this challenge (i) by using pulsed UVC technologies which dramatically increase the penetrability of UVC through matter, and (ii) by integrating the pulsed UVC technologies into a laser bronchoscope, thus allowing UVC irradiation to reach deeper into the lungs. Although the exact characteristics of such a treatment should yet to be experimentally defined, this approach might be much safer and not less efficient than LDRT.