Found 40 results
Open Access
Review
20 January 2025Adsorption and High-Value Transformation of Volatile Fatty Acids from Microbial Fermentation Products: A Review
To mitigate the aforementioned global environmental issues, the concept of carbon capture and storage is crucial in addressing the necessity for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. The buildup of volatile fatty acids during anaerobic fermentation is a primary factor contributing to the suboptimal performance or outright failure of anaerobic digestion systems. In response to the pressing demand for volatile organic acid recovery and high-value conversion, we primarily outlined the sources, recovery techniques, adsorption materials, and methods for high-value conversion of volatile fatty acids. The methods of adsorbing volatile acetic acid were presented, encompassing adsorption materials, mechanisms, and interfacial modifications of the adsorbent. Furthermore, drawing from recent research advancements, we have synthesized the high-value conversion techniques for volatile fatty acids and evaluated the research challenges and future prospects in this domain.
Open Access
Article
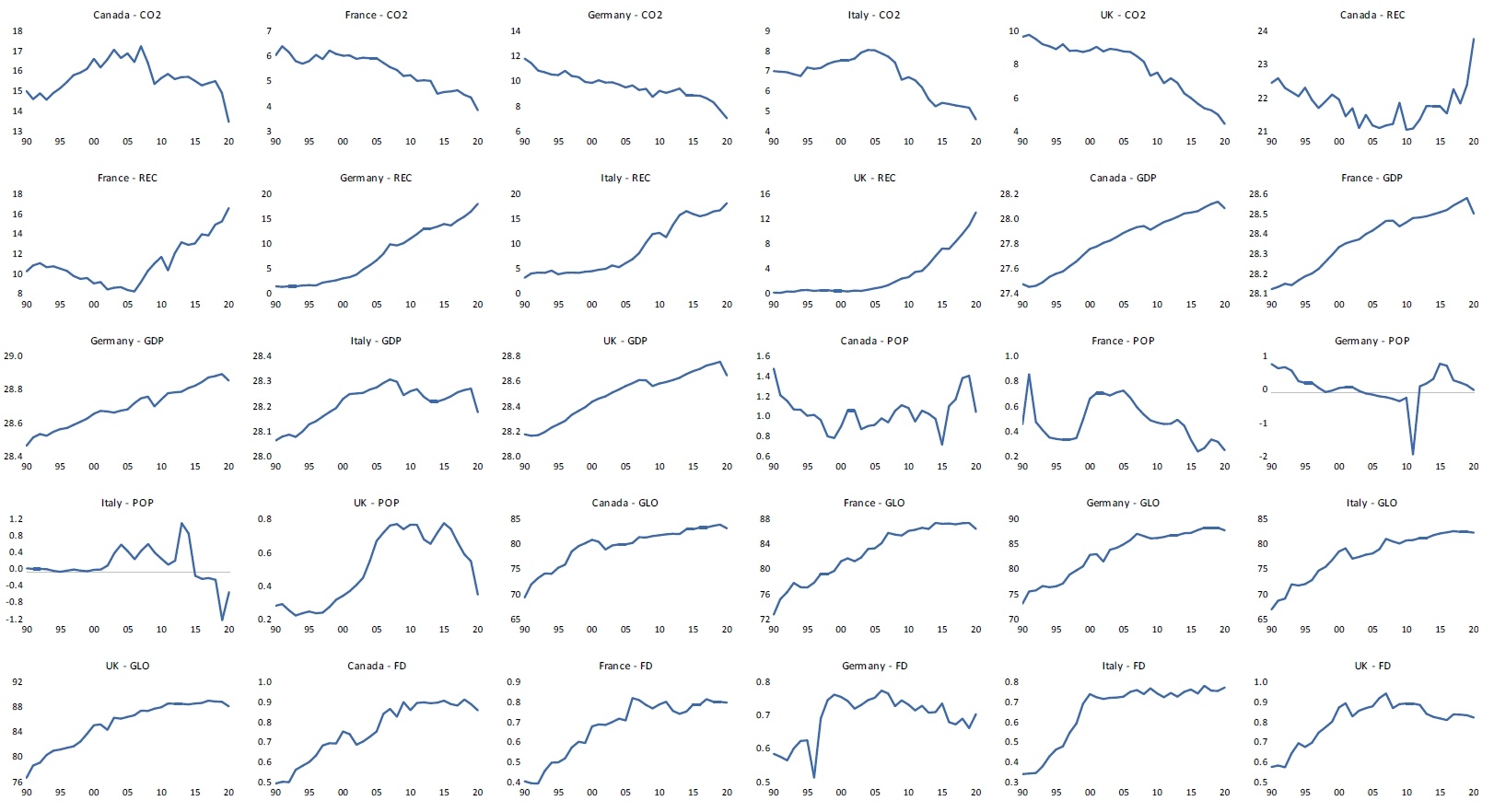
21 November 2024The Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Globalization, and Financial Development on Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Selected G7 Economies
The aggregate upsurge in carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) witnessed through environmental degradation and global climate change is a call for great concern. This, therefore, calls for the enactment, utilization and implementation of provisions and policies geared towards curbing this global economic bad without impeding global economic growth rates. This study ascertains the extent to which renewable energy consumption (REC), economic growth (GDP), population growth (POP), globalization (GLO), and financial development (FD) affect carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) in selected G7 economies (France, Germany, Canada, Italy, and the United Kingdom) from 1990–2020. The Dynamic Fixed Effect Autoregressive Distributive Lag (DFE-ARDL) and the Pooled Mean Group ARDL (PMG-ARDL) methods were employed for analysis. The empirical findings for DFE-ARDL showed that REC, GDP, and POP have an adverse association with CO2 in the long-term. However, in the short-term, REC and FD improve the environment, while GDP and POP drive CO2. It is observed that the result for REC in the short and long-run is consistent. The PMG-ARDL results revealed that REC and GLO negatively affect CO2 in the long-run, and in the short-run, GDP spurs CO2, while FD reduces it. The result summary of both methods employed demonstrates that REC, GLO, and FD benefit the environment. At the same time, GDP and POP harm the environment in the short-run but reduce CO2 in the long-run. Conclusively, the research recommends increasing the utilization of renewable energy and policies that enable economic growth and CO2 to move in the opposite direction.
Open Access
Article
18 November 2024Developing a Climate Litigation Framework: China’s Contribution to International Environmental Law
Although “climate litigation” is not an indigenous term in China, localizing it is essential to support the development of an independent environmental legal knowledge system in China. Rooted in China’s judicial tradition, which emphasizes substantive rationality, traditional legal theories have primarily focused on environmental law. However, the contemporary practices in the rule of law have created an unclear trajectory for climate litigation. Research in this area has long been trapped in a paradigm that relies on lawsuits for ecological environmental damage compensation and environmental public interest litigation, leading to a significant disconnect between theoretical framworks and practical application. With the advancement of the "dual carbon" strategic goals—carbon peaking and carbon neutrality—it has become imperative to redefine the concept of climate litigation within the Chinese context. We need to establish a theoretical framework that aligns with the “dual carbon” objectives while providing theoretical and institutional support for climate litigation, ultimately contributing to the international discourse on climate justice. Additionally, Hong Kong’s proactive climate governance and robust ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices provide valuable insights for developing comprehensive climate litigation mechanisms. Based on this analysis, we propose concrete plans for building a climate litigation system in China, establishing a preventive relief system and a multi-source legal framework at the substantive level and developing climate judicial mechanisms for mitigation and adaptation at the procedural level.

Open Access
Review
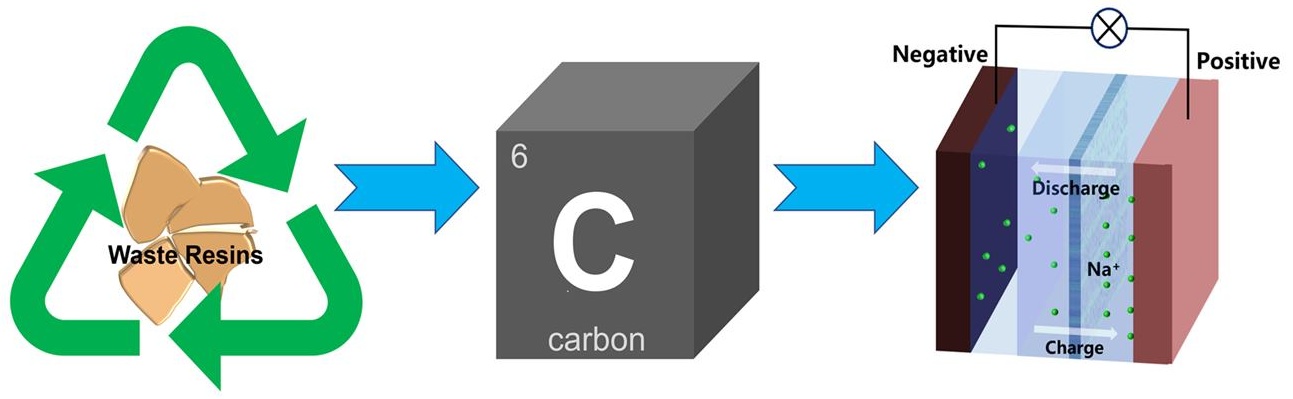
01 November 2024Waste Resin Derived Carbon Materials for Sodium-Ion Batteries
As the environmental issues caused by waste resin become increasingly severe, there is an urgent need to develop ways to handle it in a high-value and harmless manner. Turning waste resin into functional carbon materials is a realizable and promising scheme, which could be a trigger to carry forward emerging sustainable battery technologies and applications. However, there are few review articles about the basics and research progress of the waste resin derived carbon materials for sodium-ion batteries. This review article provides a brief overview mainly about resin recycling and the potential usage of the resultant carbon materials for sodium-ion batteries. Specifically, we show the potential improvements in existing research, focusing on utilization of the waste as well as the significance of new routes for resin recycling. This work offers insights for the design of sustainable carbon materials for battery systems.
Open Access
Article
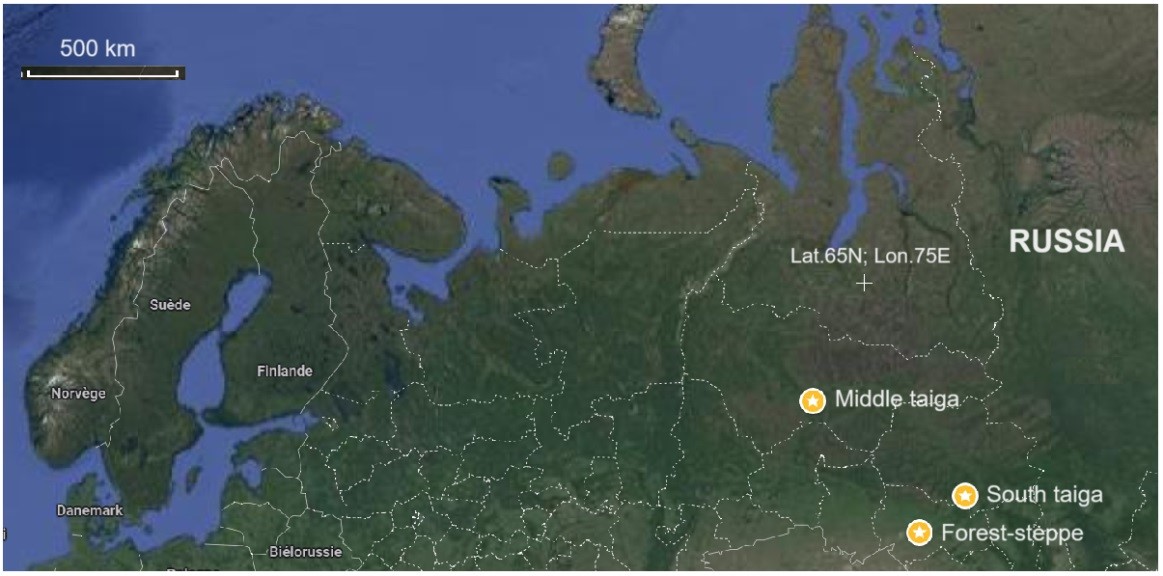
12 October 2024Production and Destruction of Plant Organic Matter in Bog Ecosystems in the South of Western Siberia
There are still many gaps in studies of the carbon cycle in northern ecosystems. It is challenging also in the context of climate change. This new study focuses on providing the state of the art data on the dynamics of plant organic matter, namely, the live plant biomass (phytomass), the dead biomass (mortmass), the Net Primary Production (NPP), as well as the rate of decomposition of plant organic matter of the major plant species, contributed to peat deposits. The study was conducted via direct in–situ measurements of different fractions of plant organic matter at a few test sites of oligotrophic pine–dwarf shrub–Sphagnum bogs at a wide geographic gradient (from the middle taiga to the forest-steppe regions in Western Siberia) based on an original methodology of measurements developed by the authors. In general, the five groups of plant species were distinguished in terms of productivity and decomposition rates. The study revealed a strong correlation between the net primary production (NPP) and the rate of decomposition of plant organic matter in pristine northern peatlands: an increase in productivity (NPPs) was basically leading to an increase in rates of decomposition in all plant materials collected in bog ecosystems. The study contributes to a global understanding of patterns and main drivers related to basic set of carbon cycle components in the northern wetland (peatland) ecosystems, their diversity and their spatial distribution.
Open Access
Review
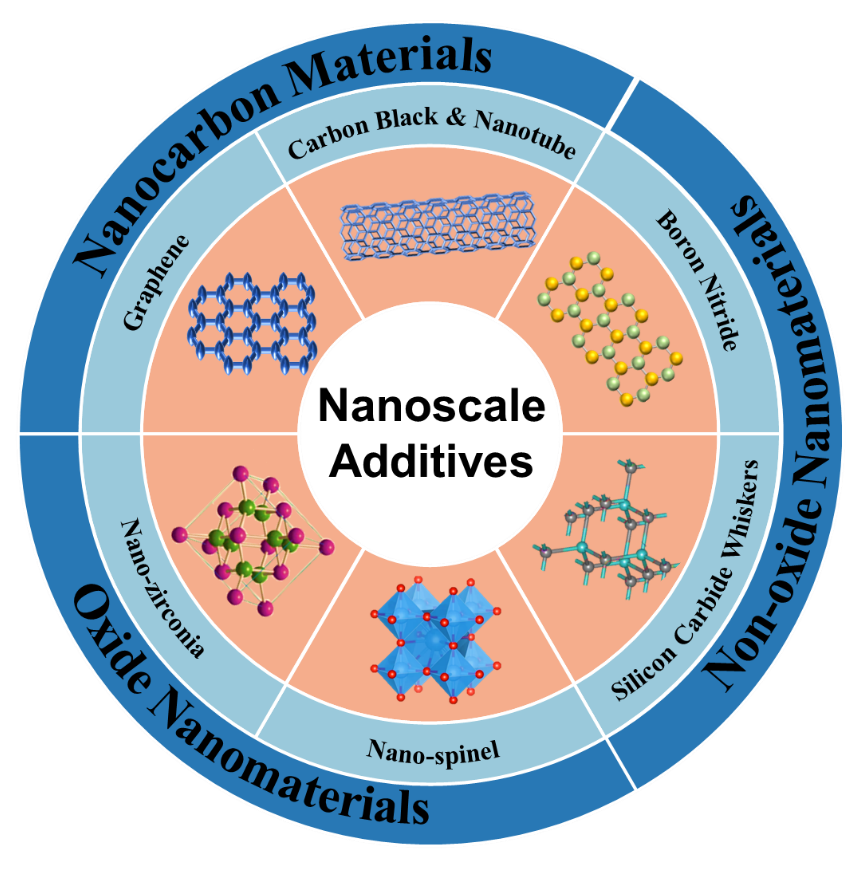
02 September 2024A Review on the Application of Nanomaterials to Boost the Service Performances of Carbon-Containing Refractories
To meet the high-quality requirements for clean steel production and fully exploit the performance advantages of carbon-containing refractories, nanomaterial has been introduced into the matrix to develop advanced carbon-containing refractories. Nanomaterials, as critical additives, play a crucial role in developing novel refractories. The service performances of carbon-containing refractories are affected not only by their physical and chemical properties but also by their microstructure. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the latest research on oxide-carbon composite refractories containing nanomaterials, categorized by their composition: nanocarbons, nano oxides, and nano non-oxides. Incorporating nanomaterials can enhance the service performances of the refractories, optimizing phase composition and microstructure. Furthermore, future research directions in nanomaterial technology for carbon-containing refractories are discussed.
Open Access
Communication
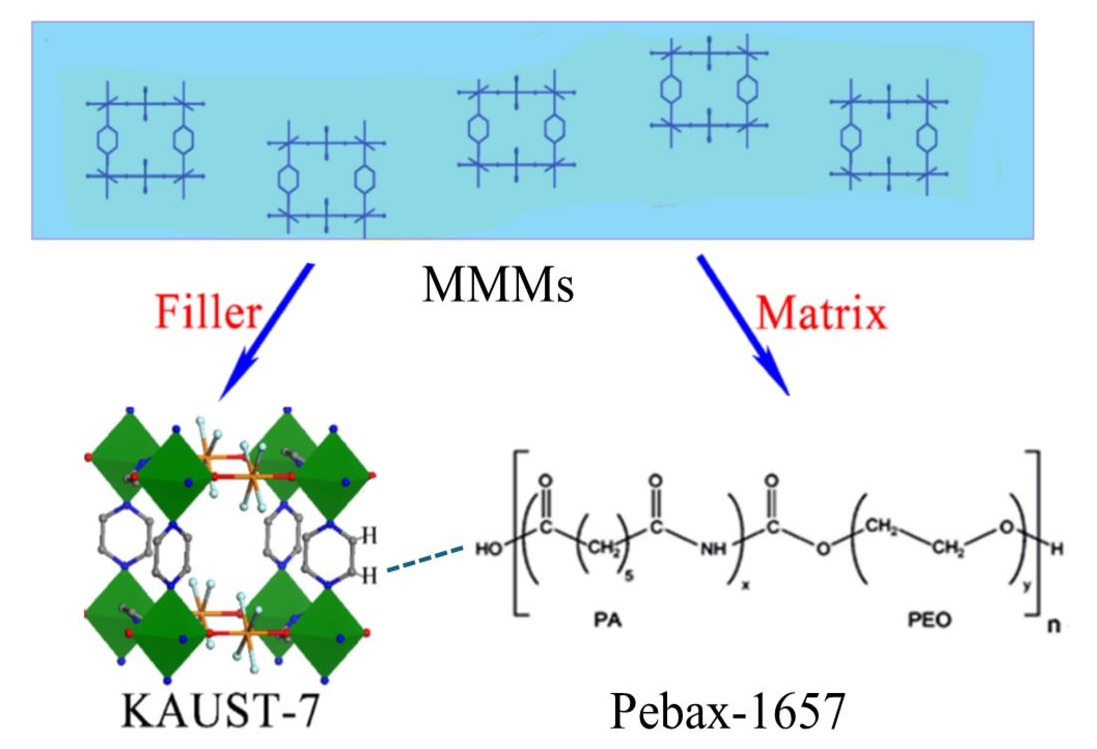
22 August 2024Mixed Matrix Membranes Produced from a Fluorinated MOF and Pebax for CO2/H2 Separation
Hydrogen (H2) emerges as a promising clean energy source, but its efficient purification from various sources needs advanced separation technologies. This study explores the use of CO2-selective membranes, especially mixed matrix membranes (MMM) incorporating KAUST-7 metal-organic framework (MOF), for hydrogen purification. The MMM was fabricated with various KAUST-7 content in a polymer matrix (Pebax 1657) and characterized via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and gas permeation tests. The XRD analysis confirms the incorporation of KAUST-7 into the MMM, while SEM reveals a homogeneous particle distribution at low content (below 10%) but agglomeration at higher ones (above 10%). FTIR confirms good interfacial interactions between the MOF and polymer matrix. TGA results show that the MMM thermal stability slightly decreases with increasing MOF content. Gas permeation results reveal improved CO2 permeability (79%) and CO2/H2 selectivity (19%) for MMM compared to neat Pebax membranes, with an optimal performance observed at 10 wt.% KAUST-7. Beyond this threshold, the performance deteriorates, possibly due to polymer rigidity and MOF agglomeration. Overall, the study highlights the potential of KAUST-7/Pebax MMM for enhanced hydrogen purification.
Open Access
Editorial
16 August 2024
Open Access
Article
26 July 2024Current and Future Costs of Storage for Electricity in a Decarbonized Electricity System
As power systems globally are transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable sources, integrating energy storage becomes imperative to balance variable renewable electricity generation. The core objective of this paper is to conduct a comprehensive cost assessment of selected energy storage technologies from 2023 to 2050, focusing on the Austrian electricity market. Our method combines techno-economic assessment with the technological learning method to integrate various storage technologies into a renewable electricity system, using scenarios that account for decarbonization goals. Results indicate that pumped storage hydro exhibits none or negative learning effects, while lithium-ion batteries demonstrate significant investment cost decreases. Despite investment cost reductions, underground hydrogen storage continues to incur high total costs per kWh discharged due to low roundtrip efficiency, suggesting its future outlook depends on seasonal storage needs in fossil-free power systems. An important finding of this analysis underscores the importance of optimizing the ratio of electricity demand, renewable generation expansion and storage deployment for cost-effectiveness. Excessive storage deployment leads to lower utilization and higher costs, emphasizing the necessity of at least 1500 full-load hours for profitable operation across all storage systems. Strategic planning for optimal storage deployment is emphasized to optimize utilization and minimize costs.
Open Access
Case Report
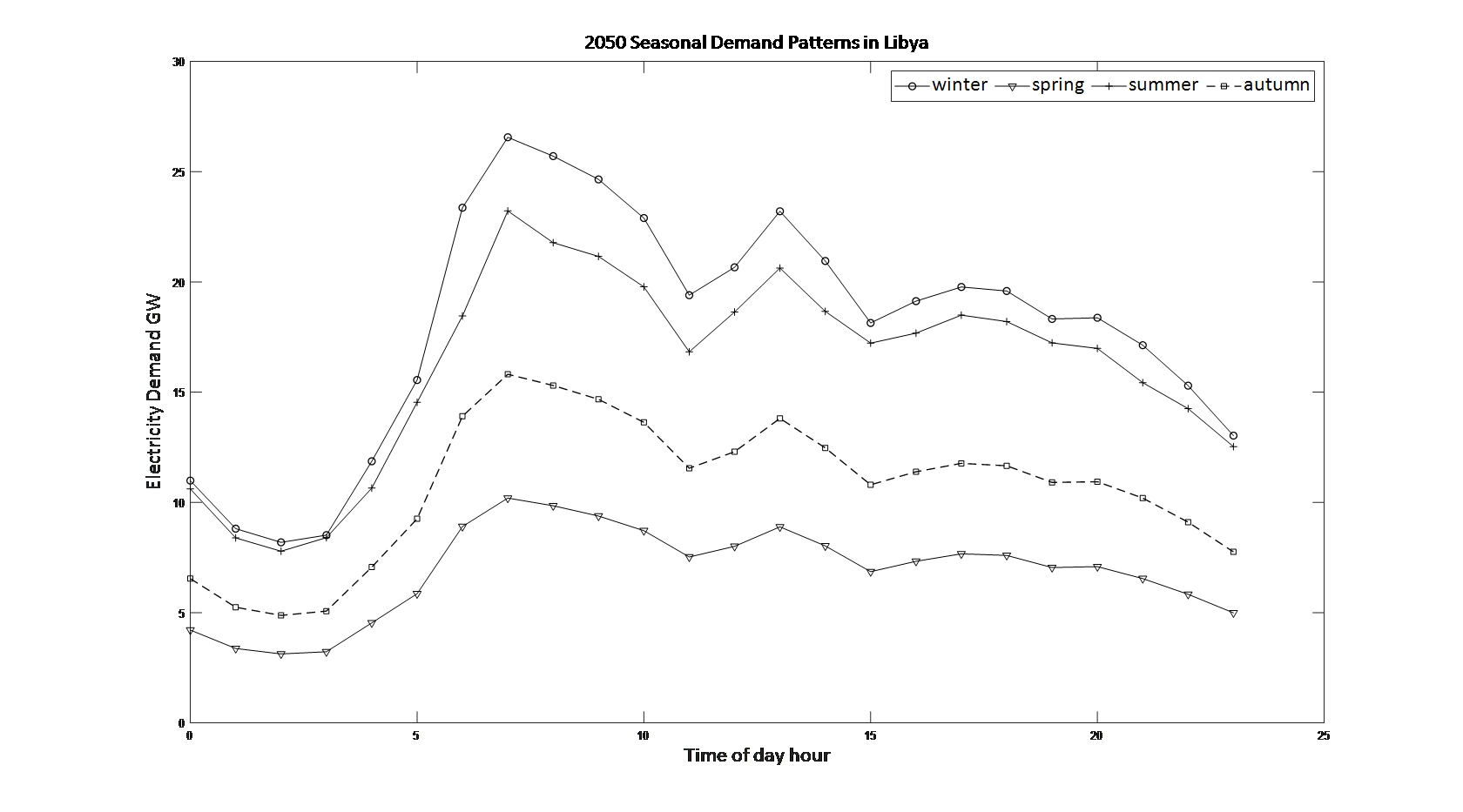
26 February 2024‘Greening’ an Oil Exporting Country: A Hydrogen and Helium Closed-cycle Gas Turbines Case Study
Holistic decarbonisation requires collaborative efforts and substantial investments across diverse economic sectors. This study introduces an innovative national approach, blending technological insights and philosophical considerations to shape decarbonization policies and practices. Libya is the case study. The proposed framework involves submersible power stations with continuous-duty helium closed-cycle gas turbines to supply electricity demand and hydrogen. Extensive national data is analysed, incorporating factors such as sectoral consumption, sea temperature, and port locations. An analytical model is developed, providing a valuable foundation for realistic decarbonization scenarios. The model aims to maintain the benefits of current energy consumption, assuming a 2% growth rate, while assessing changes in a fully green economy. The results offer qualitative and quantitative insights on hydrogen use and an expected rise in electricity demand. Two scenarios are examined: self-sufficiency and replacing oil exports with hydrogen exports. This study provides a quantitative perspective on decarbonization, focusing on a submersible helium closed cycle gas turbine concept resistant to natural disasters and proliferation. Findings underscore the substantial changes and investments needed for this transition, identifying primary needs of 27 GW or 129 GW for self-sufficiency and exports, respectively. This foundational analysis marks the start of research, investment, and political agendas toward decarbonization.