Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
12 November 2025Topological Optimization for Environmental Sustainability in Civil Engineering Structures Design
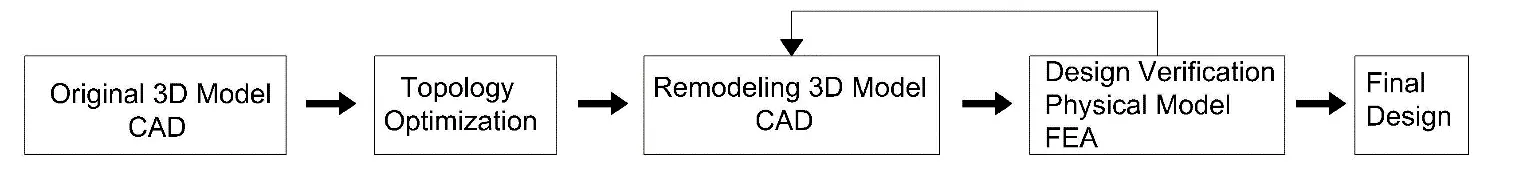
The increasing demand for sustainable and cost-efficient construction highlights the need to minimize material consumption in civil engineering structures without compromising safety or performance. This study investigates the optimization of steel purlin cross-sections in metal buildings as a means to enhance structural efficiency and environmental sustainability. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and the Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization (SIMP) method were employed to identify optimal material distributions and evaluate the effects of varying cross-section geometries. Both rectangular and IPE purlin sections were analyzed under realistic loading conditions to compare stress, deformation, and weight performance before and after optimization. The results demonstrate that substantial reductions in material mass, up to approximately 25–30%, can be achieved while maintaining nearly identical stress and displacement responses. These findings confirm that structural optimization effectively reduces both construction costs and environmental impact. The study concludes by recommending the adoption of topology and cross-section optimization techniques in the design of steel structures, particularly in public projects, to promote resource efficiency and sustainable construction practices.
Open Access
Case Report
10 November 2025Non-Fallot Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome in Fetuses: Key Insights for Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Care
Absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) is a rare cardiac malformation that is almost always associated with a Fallot-type ventricular septal defect (VSD). More rarely, it can occur with an intact ventricular septum or muscular VSD. The limited number of observations reported in the medical literature affects the quality of prenatal counselling given to the families concerned. We report 3 new cases of APVS without Fallot-type VSD, with 1 case associated with a muscular VSD, and have carried out a review of the literature on this rare malformation. Two of the fetuses had hydrops fetalis and one of these two had intra-uterine death. A 16p13.11 microduplication transmitted by the father was found in one fetus whose post-natal evolution was favorable following surgical ligation of an aneurysmal ductus arteriosus. A newborn with hydrops fetalis had a favorable outcome after spontaneous closure of the ductus arteriosus on the third day of life. Unlike Fallot-type APVS, non-Fallot type APVS is characterized antenatally by the constant presence of a large ductus arteriosus, the absence of aneurysmal pulmonary branches, a high frequency of chromosomal anomalies, but the absence of 22q11 micro deletion. After birth, early closure of the ductus may be indicated in cases of significant heart failure.

Open Access
Review
07 November 2025Value Engineering in the Era of Industry 4.0: From Gap Analysis to Research Methodologies and Strategic Framework
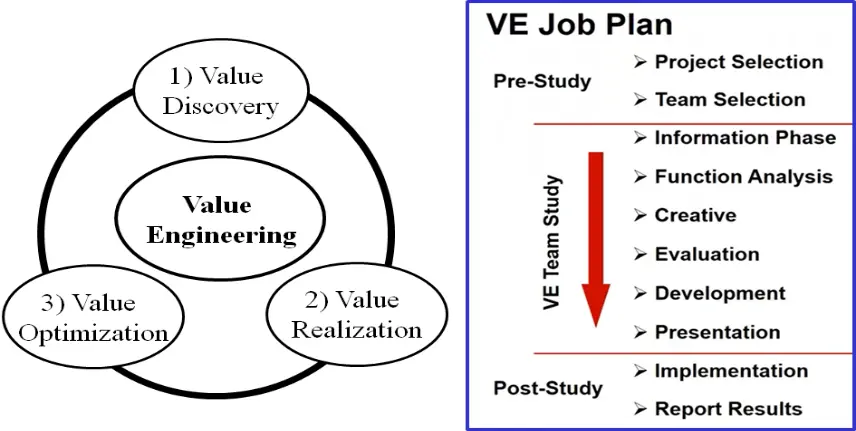
Traditional Value Engineering (VE) has long focused on optimizing the function-to-cost ratio but faces limitations in digitalized industrial contexts. Conventional VE lacks integration with advanced technologies, empirical validation in smart environments, and alignment with sustainability and circular economy objectives. The emergence of Industry 4.0—driven by cyber-physical systems, IoT, big data analytics, digital twins, and artificial intelligence—has transformed industrial ecosystems, necessitating a redefinition of VE practices. This study employs a systematic literature review and structured gap analysis to examine the evolution, applications, and challenges of VE across manufacturing, construction, supply chain, and service sectors. The analysis identifies three key deficiencies in conventional VE: (i) absence of integrated digital frameworks, (ii) limited empirical validation in smart environments, and (iii) weak incorporation of sustainability and circular economy principles. To address these gaps, Value Engineering 4.0 (VE 4.0) is proposed as a function-driven, data-intelligent, and human-centric methodology. It is structured around a six-component strategic framework: (1) digital foundations for technological readiness and organizational alignment; (2) smart VE processes leveraging AI, IoT, and advanced analytics for predictive, connected decision-making; (3) an enhanced Job Plan integrating AR/VR, NLP, and blockchain for improved speed, accuracy, and lifecycle alignment; (4) a phased implementation roadmap; (5) real-time DMAIC integration for continuous optimization; and (6) enablers covering leadership, skills, infrastructure, and cybersecurity. VE 4.0 provides both a research agenda and a practical roadmap, enabling organizations to innovate, enhance resilience, and achieve sustainable competitiveness in Industry 4.0 ecosystems.
Open Access
Article
07 November 2025Parking Space Detection Using a Machine Learning-Enhanced Unmanned Aerial Vehicle in a Virtual Environment
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have increased in popularity for several diverse applications over the past few years. Parking, especially in crowded parking lots, can be very time-consuming, as a driver must manually search for vacant spaces among many occupied ones. In this work, reinforcement learning—a category of machine learning in which an agent receives inputs from the environment while outputting actions in order to maximize reward—was utilized in tandem with AirSim, a drone simulator developed by Microsoft, to automate a virtual UAV’s movement. A convolutional neural network (CNN) was then utilized to detect both vacant and filled parking spots, which achieved 98% recall and 93% accuracy. Unreal Engine was used to create a custom environment that resembled a parking lot, and the virtual drone was trained using a Deep Q-Network (DQN). The DQN achieved a mean reward of 394.5 in training and 460.4 in evaluation. A pre-trained CNN integrated with the DQN enables the real-time classification of vacant/occupied parking spaces from drone imagery. Results validate the effectiveness of combining reinforcement learning navigation with CNN image classification, demonstrating deployment-ready performance for real-world congested parking applications.

Open Access
Article
06 November 2025Sustainable Recycling Mechanisms for Waste Cooking Oil in China’s Third-Tier Cities: Evidence from Restaurant Practices
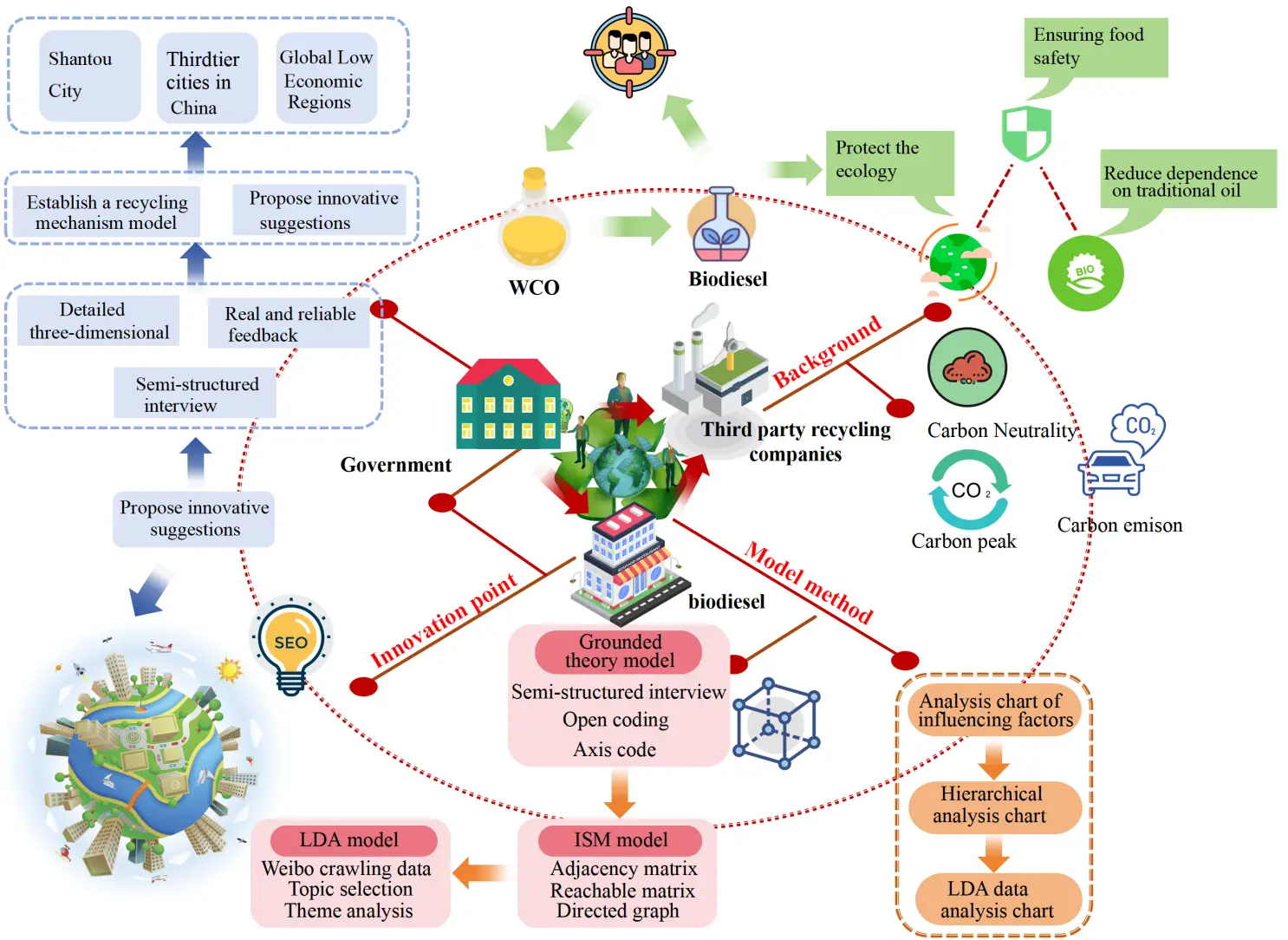
The conversion of waste cooking oil (WCO) into biodiesel is a key strategy for advancing energy sustainability, particularly within China’s rapidly expanding restaurant industry. In third-tier cities such as Shantou, Guangdong Province, WCO collection faces unique challenges. Through in-depth interviews with 20 restaurant operators, this study identifies multiple barriers to effective WCO management, including an aging population, underdeveloped local economies, limited technological infrastructure, and unequal access to educational opportunities, all of which hinder the adoption of advanced filtration systems and broader environmental sustainability initiatives. Moreover, the non-standardized operations of third-party WCO collection services, coupled with space constraints in small restaurant kitchens, further exacerbate inefficiencies in recovery processes. To address these challenges, this study develops a comprehensive framework for WCO collection that is adaptable to regions with similar socio-economic conditions. Integrating grounded theory, Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM), and Latent Dirichlet Allocation, the framework fills critical gaps in existing research. The analysis reveals that government financial incentives occupy the foundational layer of the ISM hierarchy and serve as a key driver of recycling behavior among restaurant operators; educational attainment enhances awareness and compliance but is moderated by structural constraints; and trust in third-party recyclers exerts a relatively limited influence. Correspondingly, H1 receives qualitative support, H2 is partially supported, and H3 gains only limited support. Building on these findings, the study proposes a multi-stakeholder governance framework that includes a “community-school-family” education system, an intelligent third-party management platform, and a government-led industrial chain to promote the formation of a closed-loop circular economy. The results demonstrate that the proposed framework not only offers actionable policy recommendations but also facilitates the adoption of sustainable practices and deepens the understanding of socio-economic and operational factors affecting WCO management, thereby providing strong support for energy and environmental sustainability.
Open Access
Communication
05 November 2025Computer Simulation of the Heat Treatment of Knitting Needles
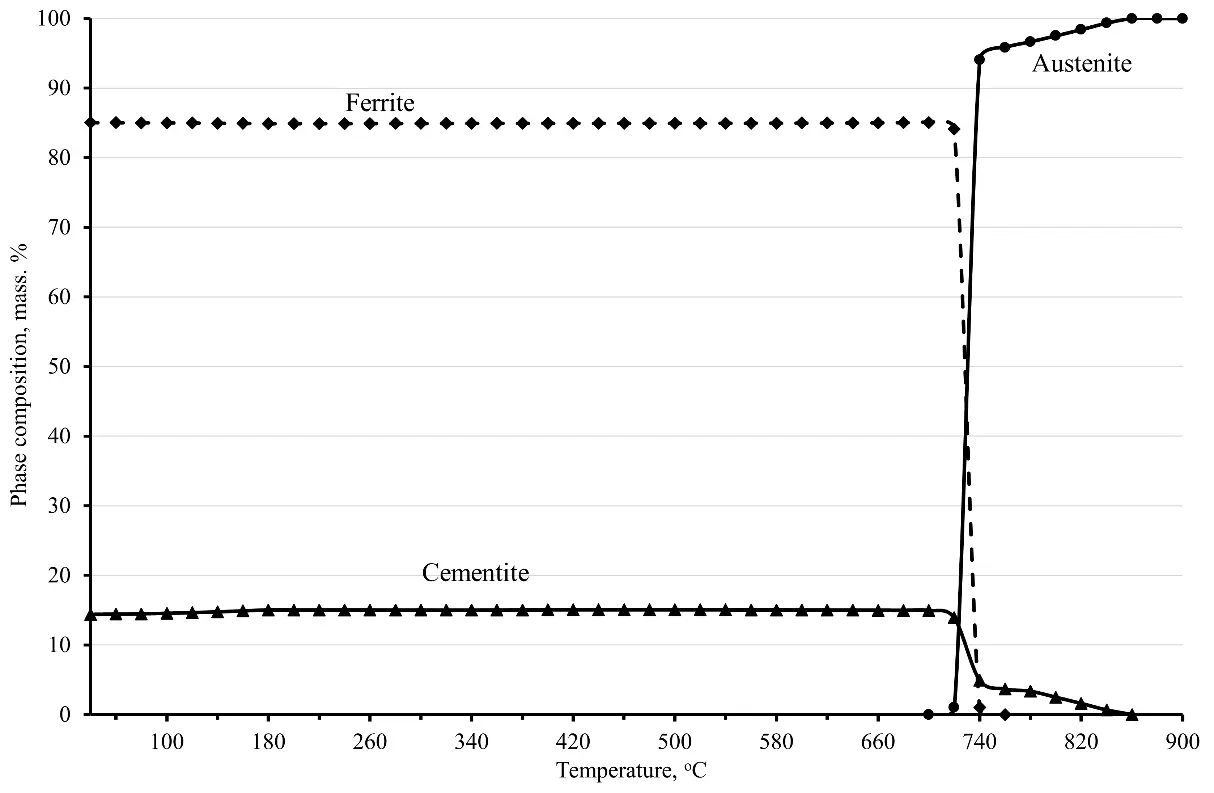
The article discusses the main steels that are used to make needles for knitting machines. Based on an analysis of literature data, needles for knitting machines are primarily made of high-carbon steel, the main alloying elements of which are carbon in an amount of about 1.0 wt. %, silicon (0.3–0.5 wt. %), manganese (0.55–0.75% by weight), and chromium (about 0.4% by weight). In addition, these steels may contain microalloying additives, such as niobium in an amount of about 0.010% by weight. The publicly available computer model has been expanded to simulate the heat treatment of new materials for knitting machine needles. Using the developed computer model, the optimal structural and phase composition of the knitting needle material is established, which confirms its performance characteristics. It is shown that computer simulation of heat treatment modes makes it possible to conduct computer simulations of heat treatment modes with good accuracy and evaluate the effect of optimizing heat treatment parameters to obtain the best properties. Based on the results of computer modeling, one or more promising heat treatment modes can be selected, which can ultimately have a positive effect on the quality and service life of knitting needles.
Open Access
Review
04 November 2025Tools and Strategies for Engineering Bacillus methanolicus: A Versatile Thermophilic Platform for Sustainable Bioproduction from Methanol and Alternative Feedstocks
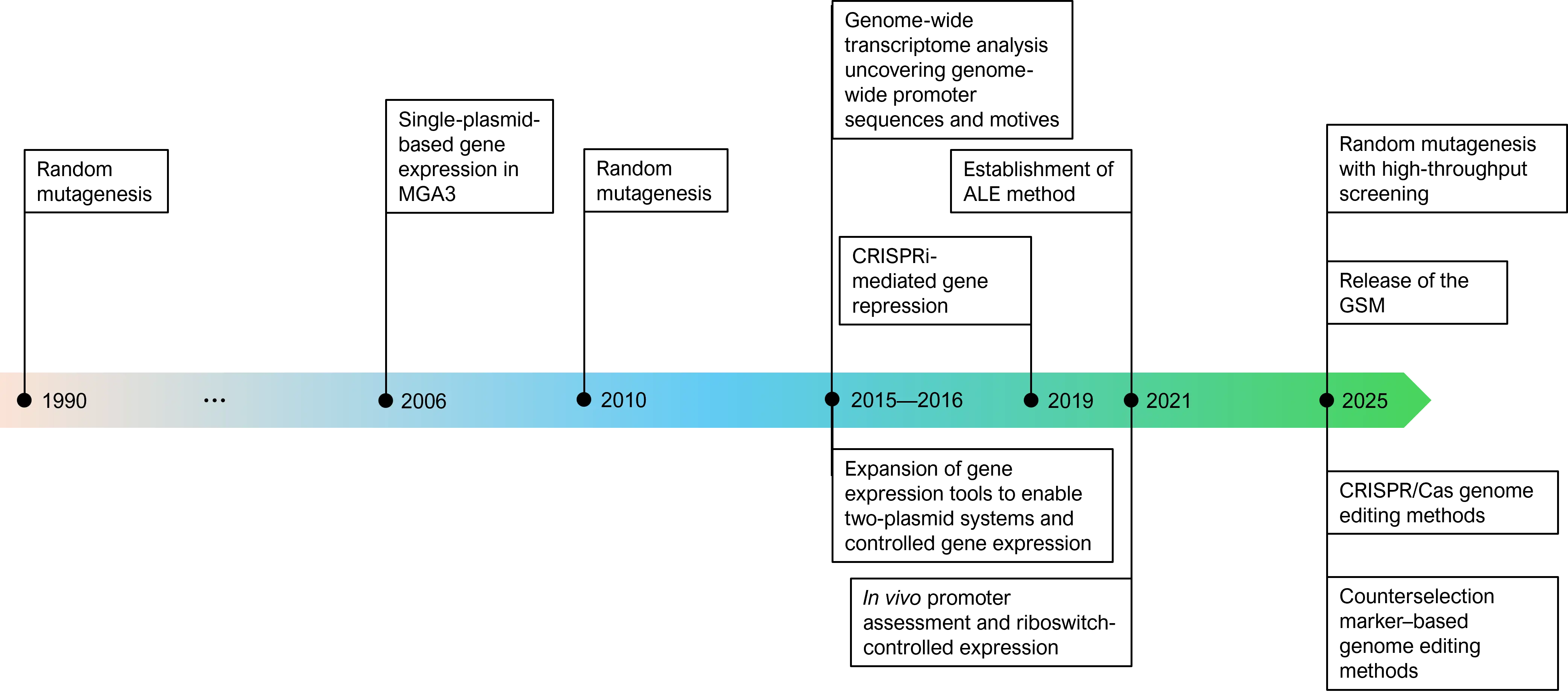
Bacillus methanolicus MGA3 is a methylotrophic bacterium with a high potential as a production host in the bioeconomy, particularly with methanol as a feedstock. This review presents the recent acceleration in strain engineering technologies through advances in transformation efficiency, the development of CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing, and the application of genome-scale models (GSMs) for strain design. The generation of novel genetic tools broadens the biotechnological potential of this thermophilic methylotroph. B. methanolicus is a facultative methylotroph and apart from methanol it can grow on mannitol, arabitol and glucose, and was engineered for starch and xylose utilisation. Here, the central carbon metabolism of B. methanolicus for various native and non-native carbon sources is described, with an emphasis on methanol metabolism. With its expanding product portfolio, B. methanolicus demonstrates its potential as a microbial cell factory for the production of tricarboxylic acid(TCA) cycle and ribulose monophosphate (RuMP) cycle intermediates and their derivatives. Beyond small chemicals, B. methanolicus is both a valuable source of novel thermostable proteins and a host for the production of heterologous proteins, enabled by advances in genetic tools and cultivation methods. Continued progress in understanding its physiology and refining its genetic toolbox will be decisive in transforming B. methanolicus from a promising candidate into a fully established industrial workhorse for sustainable methanol-based biomanufacturing.
Open Access
Article
03 November 2025Sequential Thermal and Optical Upgrades for Passive Solar Stills: Toward Sustainable Desalination in Arid Climates
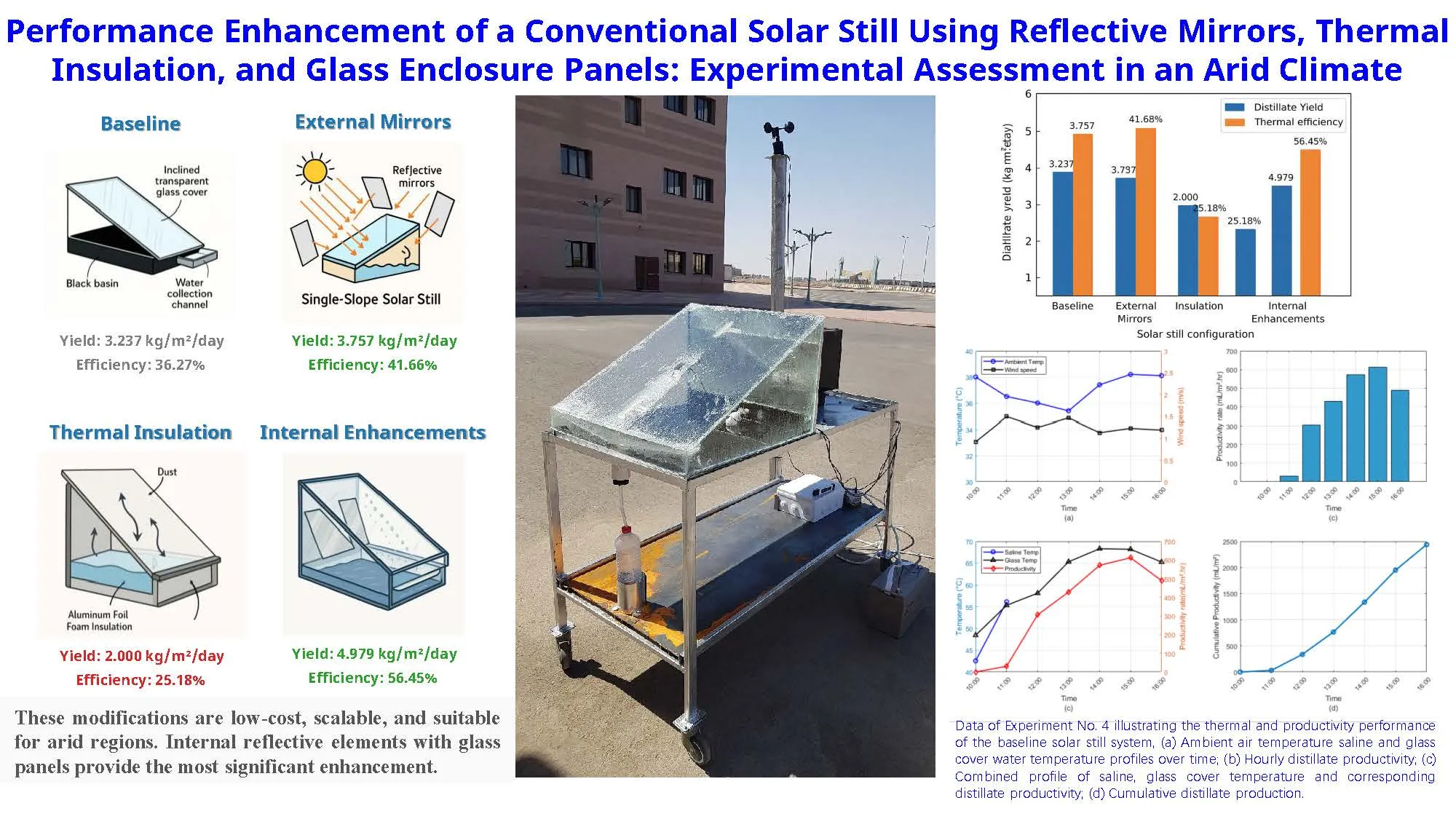
This study investigates the thermal performance and freshwater productivity of a passive single-slope solar still under four distinct configurations, aimed at enhancing distillation efficiency using low-cost modifications. The experiments were conducted in Tabuk, Saudi Arabia (28°23′50″ N, 36°34′44″ E), a region characterized by high solar irradiance ranging from 847 to 943 W/m2. The baseline system, constructed with a stainless-steel basin and inclined transparent glass cover, served as the control, achieving a cumulative distillate yield of 3.237 kg/m2/day and a thermal efficiency of 36.27%. Subsequent modifications included the addition of external reflective mirrors (Experiment 2), aluminum foil foam insulation (Experiment 3), and internal enhancements with side glass panels and internal aluminum mirrors (Experiment 4). Results demonstrated that the external mirror modification improved the distillate yield by 16% to 3.757 kg/m2/day, with a corresponding efficiency of 41.66%. However, insulation under dusty conditions led to a reduced yield of 2.000 kg/m2 and an efficiency of 25.18%, highlighting the critical influence of solar transmittance. The most notable improvement was recorded in the fourth configuration, which combined internal reflective elements and transparent side panels, resulting in a maximum yield of 4.979 kg/m2/day and thermal efficiency of 56.45%. These findings confirm that optical and thermal design enhancements can significantly augment the performance of passive solar stills, especially under high-irradiance, clear-sky conditions. The proposed modifications are low-cost, scalable, and suitable for implementation in remote and arid regions facing freshwater scarcity. This study offers valuable insights into the systematic optimization of solar distillation systems to improve sustainable water production.
Open Access
Communication
31 October 2025Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on PA Pressures in D-TGA after Atrial Switch Operations
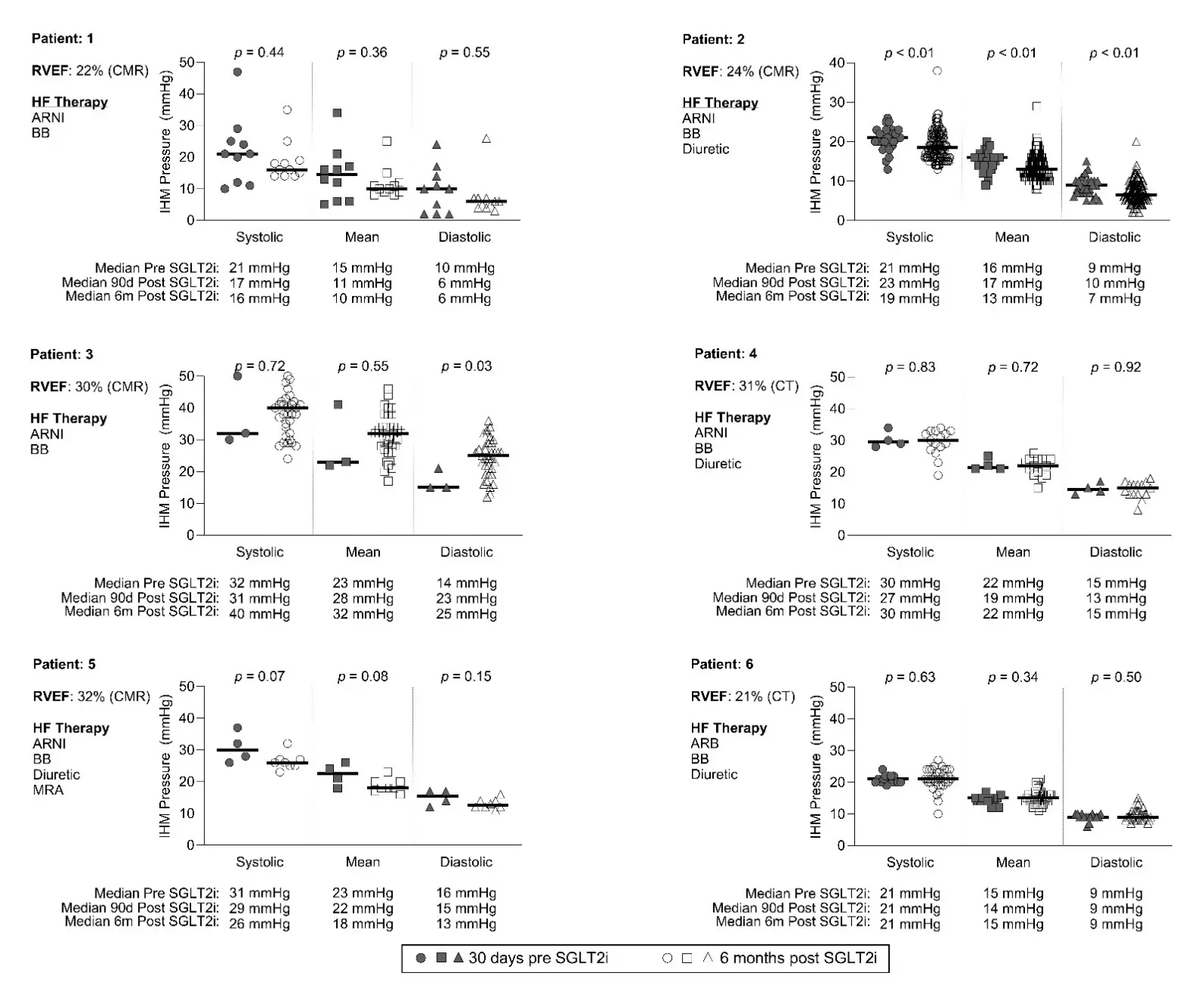
Heart failure (HF) is the leading cause of mortality in adults with congenital heart disease (ACHD), including patients with systemic right ventricles, such as those with dextro-transposition of the great arteries with an atrial switch (DTGA-AS). With more ACHD patients surviving well into adulthood, there is an increase in advanced heart failure (HF) and pulmonary hypertension (PH), many of whom are being treated with SGLT2-inhibitors (SGLT2-i). However, there is a paucity of data supporting SGLT2-i inhibitor use in the ACHD population and on how they may impact pulmonary artery pressures (PAP). This single center retrospective study aimed to evaluate the impact of SGLT2-i on (PAP) in patients with DTGA-AS. Six patients were studied, all male (mean age 41 [range 38–52] years), with a mean systemic right ventricular ejection fraction of 27% (range 22–32%), with an implanted hemodynamic CardioMEMs monitor data were recorded one month prior to medication start and six months afterwards. Half of the patients had normal PAP, and the addition of SGLT2i did not result in a significant change in PAP in all patients. However, half of the patients demonstrated a trend towards improvement. In conclusion, in this study with a small sample size of DTGA-AS patients, there was no significant reduction in PAP.
Open Access
Article
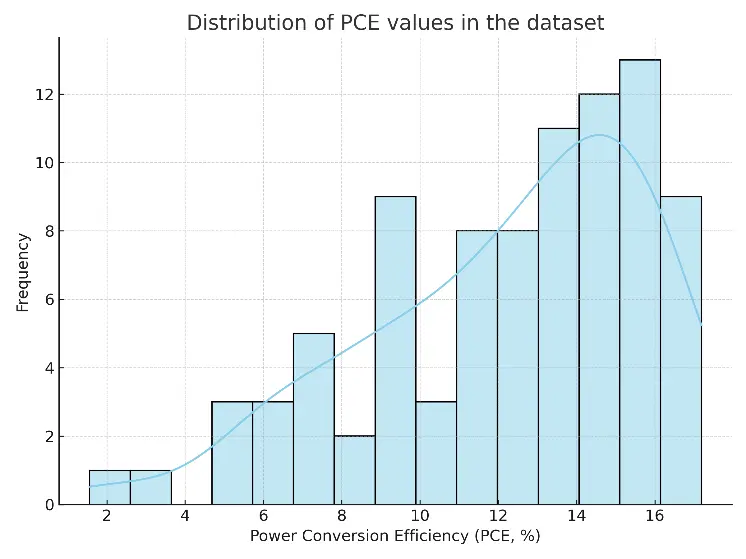
31 October 2025Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Organic Photovoltaic Efficiency
This study forecasts the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of organic solar cells using data from experiments with donors and non-fullerene acceptor materials. We built a dataset that includes both numerical and categorical features by using standard scaling and one-hot encoding. We developed and compared several machine learning (ML) models, including multilayer perceptron, random forest, XGBoost, multiple linear regression, and partial least squares. The modified XGBoost model performed best, achieving a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 0.564, a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.446, and a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.980 on the test set. We also assessed the model’s ability to generalize and its reliability by examining learning curve trends, calibration curve analysis, and residual distribution. Plots of feature correlation and permutation importance showed that ionization potential and electron affinity were key predictors. The results demonstrate that with proper tuning, gradient boosting methods can provide highly accurate and easy-to-understand predictions of organic solar cell efficiency. This work establishes a repeatable machine learning process to quickly screen and thoughtfully design high-efficiency photovoltaic materials.