Found 15 results
Open Access
Review
18 February 2025Digital Twin and Artificial Intelligence in Machining: A Bibliometric Analysis
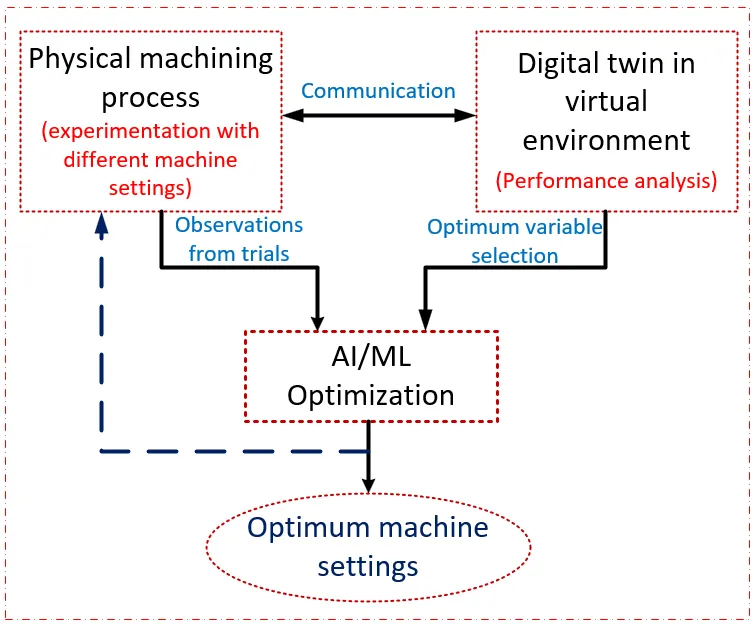
The past decade has witnessed an exodus toward smart and lean manufacturing methods. The trend includes integrating intelligent methods into sustainable manufacturing systems purposely to improve the machining efficiency, reduce waste and also optimize productivity. Manufacturing systems have seen transformations from conventional methods, leaning towards smart manufacturing in line with the industrial revolution 4.0. Since the manufacturing process encompasses a wide range of human development capacity, it is essential to analyze its developmental trends, thereby preparing us for future uncertainties. In this work, we have used a Bibliometric analysis technique to study the developmental trends relating to machining, digital twins and artificial intelligence techniques. The review comprises the current activities in relation to the development to this area. The article comprises a Bibliometric analysis of 464 articles that were acquired from the Web of Science database, with a search period until November 2024. The method of obtaining the data includes retrieval from the database, qualitative analysis and interpreting the data via visual representation. The raw data obtained were redrawn using the origin software, and their visual interpretations were represented using the VOSviewer software (VOSviewer_1.6.19). The results obtained indicate that the number of publications related to the searched keywords has remarkably increased since the year 2018, achieving a record maximum of over 80 articles in 2024. This is indicative of its increasing popularity. The analysis of the articles was conducted based on the author countries, journal types, journal names, institutions, article types, major and micro research areas. The findings from the analysis are meant to provide a bibliometric explanation of the developmental trends in machining systems towards achieving the IR 4.0 goals. Additionally, the results would be helpful to researchers and industrialists that intend to achieve optimum and sustainable machining using digital twin technologies.
Open Access
Review
13 February 2025High-Temperature Catalytic Platform Powered by Thermophilic Microorganisms and Thermozymes
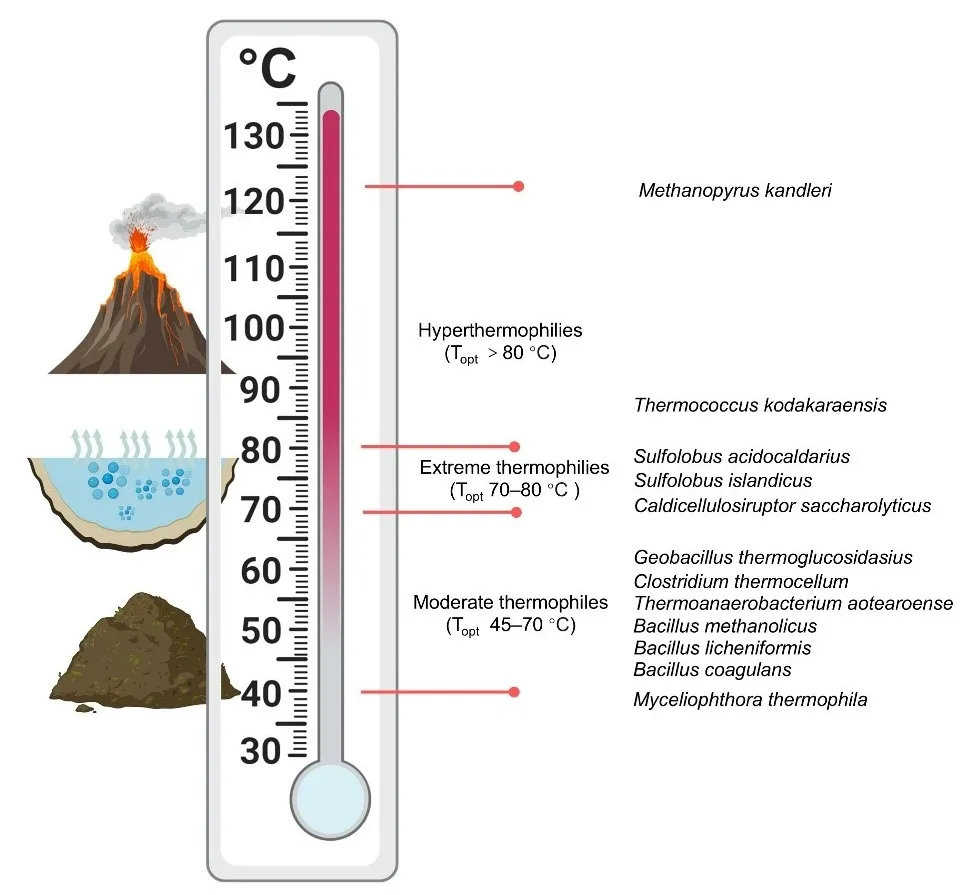
Thermophilic microorganisms, capable of thriving under high temperatures, are emerging as key platforms for next-generation industrial biotechnology (NGIB), driving innovations in lignin biorefining, bioplastics synthesis, biodiesel production, and environmental remediation. Enzymes derived from thermophilic microorganisms, thermozymes, exhibit remarkable stability and efficiency under extreme conditions, making them highly suitable for diverse industrial applications. This review highlights recent advances in leveraging thermophilic microorganisms and thermozymes for high-temperature catalysis, focusing on their economic and environmental benefits. It also emphasizes progress in high-throughput screening and artificial intelligence (AI), which have revolutionized the bioprospecting, engineering, and application potential of thermozymes. Challenges and potential solutions for industrial implementation of high-temperature catalytic platforms are also discussed, highlighting their transformative impact on sustainable biotechnology.
Open Access
Review
14 January 2025Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Sustainable Manufacturing: Current Trends and Future Prospects
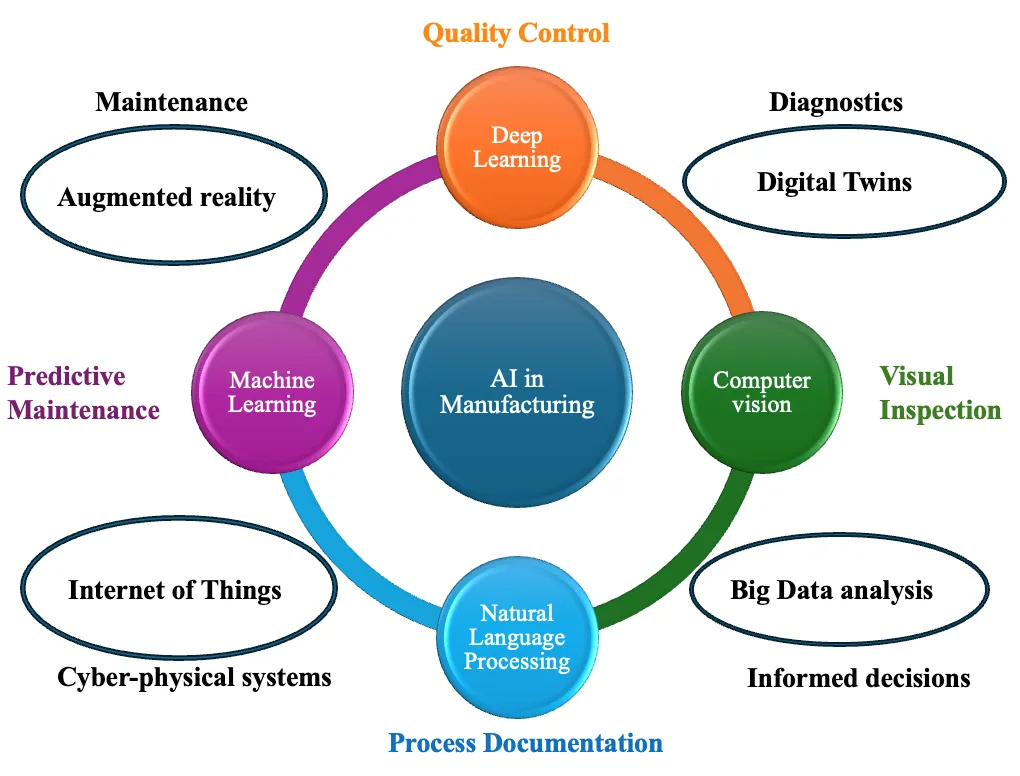
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming manufacturing processes, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance sustainability and environmental stewardship. This comprehensive review analyzes the transformative impact of AI technologies on sustainable manufacturing, focusing on critical applications, including energy optimization, predictive maintenance, waste reduction, and circular economy implementation. Through systematic analysis of current research and industry practices, the study examines both the opportunities and challenges in deploying AI-driven solutions for sustainable manufacturing. The findings provide strategic insights for researchers, industry practitioners, and policymakers working towards intelligent and sustainable manufacturing systems while elucidating emerging trends and future directions in this rapidly evolving field.
Open Access
Article
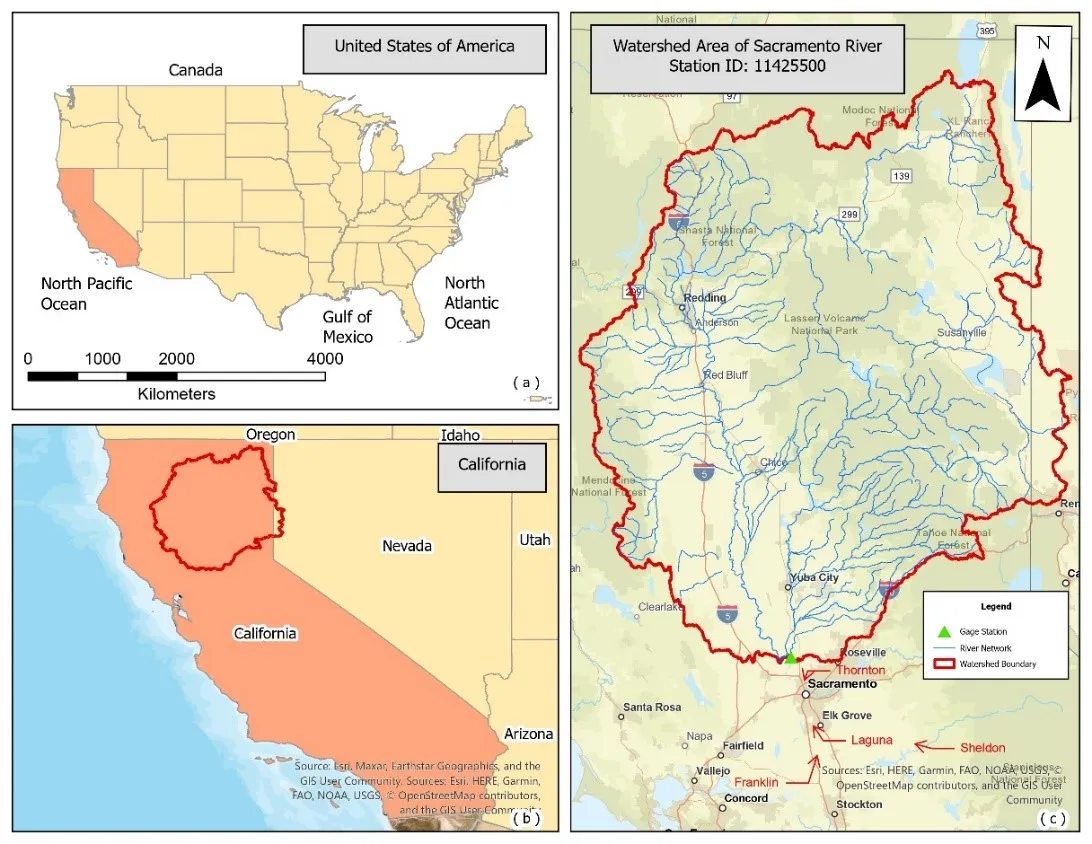
31 October 2024Analyzing Climate Dynamics and Developing Machine Learning Models for Flood Prediction in Sacramento, California
Climate change is leading to rapid environmental changes, including fluctuating precipitation and water levels, which raises the risk of flooding in coastal and riverine locations around the United States. This study focuses on Sacramento, California, a city significantly affected by these changes and recent severe flooding disasters. The ultimate goal is to understand the climate dynamics and create a more robust model to alert Sacramento and other communities to possible flooding and better prepare them for future climatic uncertainty. In this research, four classification machine learning models—Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)—are examined for their capacity to predict the occurrence of floods using historical precipitation temperature and soil moisture data. Our results demonstrate that the LSTM model, with an accuracy of 89.99%, may provide better reliable flood predictions, possibly due to its ability to process complicated temporal data. SVM, RF, and ANN showed accuracies of 81.25%, 83.75%, and 85%, respectively. The study explores the correlation between increasing precipitation incidents and severe climate variations, such as the El Niño and La Niña cycles, which could have increased flooding risks. Significant rainfall peaks occurred in 1998 and 2007, indicating that external atmospheric circumstances might have considerably impacted local weather patterns. While LSTM models show potential, there remains room to improve their accuracy and adaptability in extreme flood scenarios. Given these findings, future research could combine multiple environmental data sources and hybrid modeling approaches to enhance predictions.
Open Access
Perspective
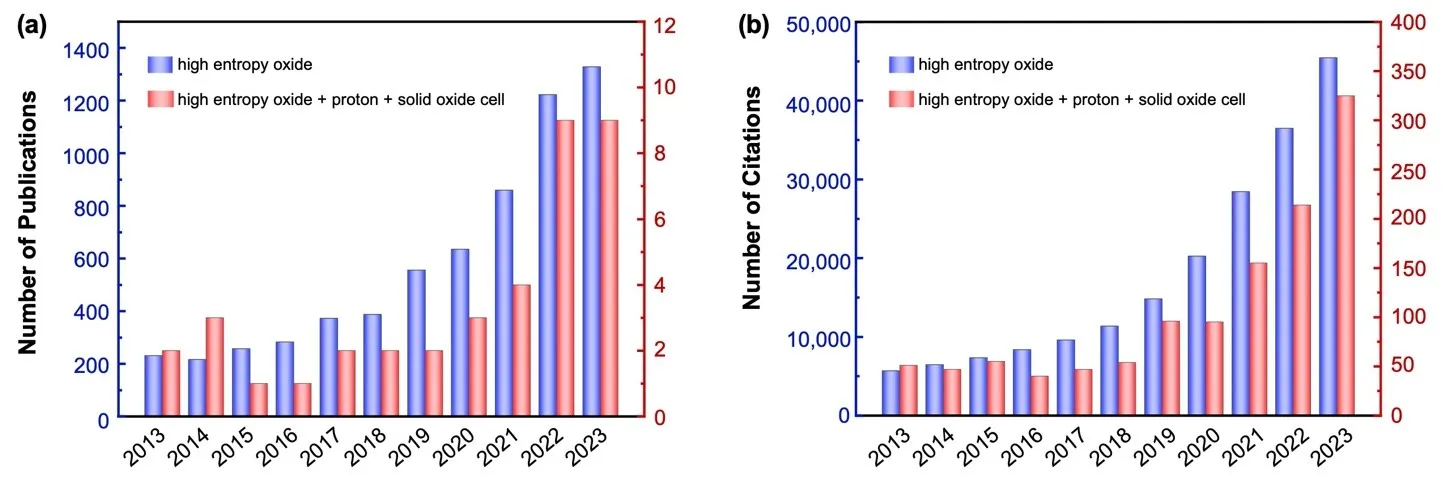
24 June 2024High Entropy Oxides: Next-Generation Air Electrodes for Reversible Protonic Solid Oxide Cells
Reversible protonic solid oxide cell (P-SOC) operating at intermediate-temperature exhibits excellent potential as a power generation and green hydrogen production device in fuel cell and electrolysis cell modes because of the high conversion efficiency. However, the lack of efficient air electrodes is the main challenge to obtain P-SOC with remarkable performance. Typically, air electrodes should possess high proton, oxygen ion and electron conductivity, outstanding catalytic ability for oxygen reduction reaction and H2O splitting, and also long-term durability. Recently, high entropy oxides (HEO) have become popular due to their various potential applications in terms of outstanding properties, including catalysis ability, conductivity, thermal stability, etc. HEO air electrodes have been confirmed to show good electrochemical performance in P-SOC, but the complex compositions and structure make it difficult to study HEO by traditional experimental methods. Machine learning (ML) has been regarded as a powerful tool in materials research and can solve the drawbacks in the discovery of HEO in a traditional way. In this perspective, we not only discuss the current utilization of HEO in P-SOC but also provide a possible process to use ML to guide the development of HEO.