Found 2 results
Article
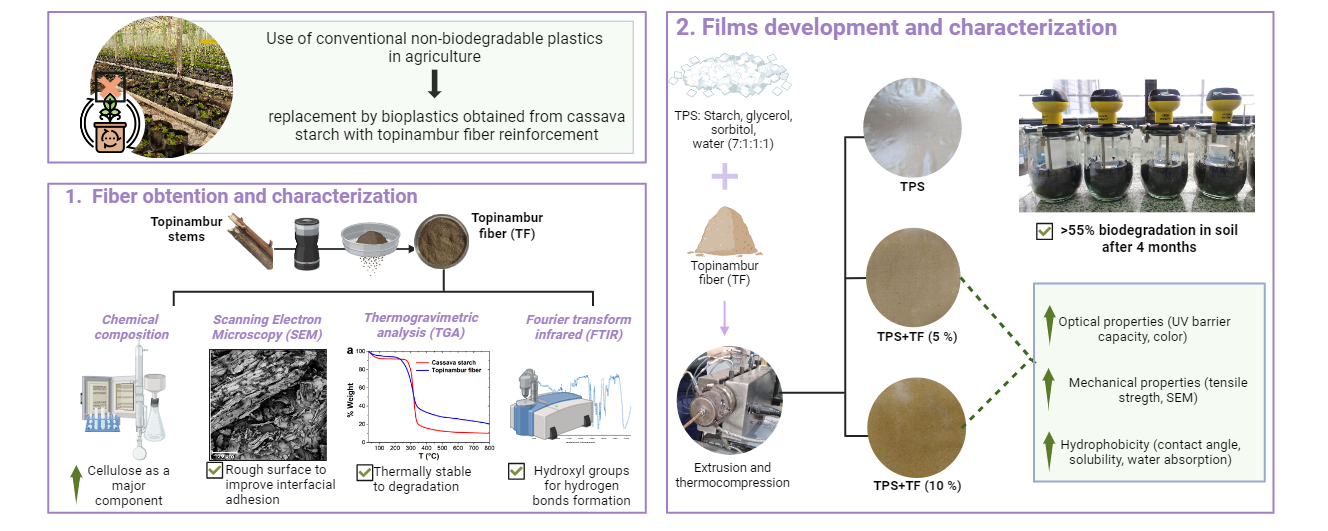
18 April 2024Biodegradable Composite Materials Based on Cassava Starch and Reinforced with Topinambur (Helianthus tuberosus) Aerial Part Fiber
The cultivation of topinambur (Helianthus tuberosus) has aroused the interest of producers since it is a source of inulin and can be used for biofuel production. During tuber processing, the aerial part of the crop remains as a by-product with no practical application. This work aimed to characterize the fibers obtained from the aerial part of topinambur and to evaluate their reinforcing potential in cassava starch-based films. Starch-based films with topinambur fiber (0, 5, and 10%) were prepared by extrusion followed by thermocompression. Topinambur residue contains 88.6% of total fiber, 8.5% ash, and 0.68% lipid. Mechanical film properties evidenced the reinforcement action of topinambur fiber, 10% content was able to increase up to 70% the Young’s modulus. SEM micrographs evidenced the good fiber-matrix interaction. UV-visible capacity, opacity, and chromaticity parameters of TPS films increased with fiber content in the formulation. Fiber incorporation improved the hydrophobicity of the biocomposite materials by increasing the contact angle. Starch-based films biodegraded more than 55% after 110 days, showing a similar trend to that of microcrystalline cellulose. Thus, topinambur residue can be effectively used as a reinforcing agent for TPS materials, being an innovative and non-toxic additive within the circular economy premises.
Article
29 January 2024The “Global Change Data Base” GCDB Facilitates a Transition to Clean Energy and Sustainability
This article presents the opportunities for constructing a global data base picturing underlying trends that drive global climate change. Energy-related CO2 emissions currently represent the key impact on climate change and thus become here the object of deep, long-term and historiographic analysis. In order to embrace all involved domains of technology, energy economy, fuel shares, economic efficacity, economic structure and population, a “Global Change Data Base” (GCDB) is suggested, based on earlier worldwide accepted data repositories. Such a GCDB works through regressions and statistical analysis of time series of data (on extensive magnitudes such as energy demand, population or Gross Domestic Product, GDP) as well as generation of derived data such as quotients of the former, yielding intensive magnitudes that describe systems and their structural properties. Moreover, the GCDB sets out to compute the first and second time derivatives of said magnitudes (and their percentual shares) which indicate new long-term developments already at very early phases. The invitation to participate in this foresight endeavour is extended to all readers. First preliminary GCDB results quantitatively portray the evolutionary structural global dynamics of economic growth, sectoral economic shifts, the shifts within energy carriers in various economic sectors, the ongoing improvements of energy intensity and energy efficiency in many economic sectors, and the structural changes within agricultural production and consumption systems.
